强化学习实验
倒双摆的DDPG
mujoco是一个物理引擎,全称为Multi-Joint dynamics with Contact,gym可以调。
这里实验一个倒双摆:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
import gymnasium as gym
env = gym.make('InvertedDoublePendulum-v5')
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0] # 9
action_dim = env.action_space.shape[0] # 1
action_bondary = env.action_space.high[0] # 1
env.action_space # Box(-1.0, 1.0, (1,), float32)
env.observation_space # Box(-inf, inf, (9,), float64)
env.env.env.env.model.nv # 3 自由度?
env.env.env.env.model.opt.gravity # array([ 1.00e-05, 0.00e+00, -9.81e+00]) 重力加速度
env.env.env.env.model.dof_damping # array([0.05, 0.05, 0.05]) 阻尼?
从文档里可以看到,状态空间有9维,第1个是小车的位置,第2-5是车和杆以及两杆之间的角度正弦和余弦,第6个是车的速度,第7-8是两个夹角的角速度。动作空间是施加给车的力,范围为-1~1。初始状态车有一个位置和速度的随机扰动。
奖励函数为10-0.01x^2^+(y-2)^2^-0.001w~1~^2^-0.005w~2~^2^,其中(x,y)为杆的顶端的坐标,最高为1.2,w~1~和w~2~是两个铰链的角速度。当y<1时环境即终止。
这里打算用DDPG,一来它是确定性的,我不希望它最终策略在稳定的时候还在不停地乱晃;二来它的损失函数比PPO好算一些。经验回放和软更新也很受用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
agent = DDPG(
state_dim,
action_dim,
action_bondary=action_bondary,
actor_lr=1e-3,
critic_lr=1e-3,
batch_size=64,
gamma=0.99,
tau = 0.02,
)
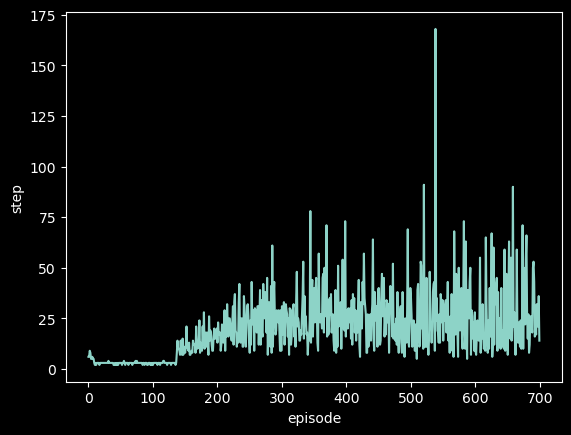
复用之前的代码(附在本节最后),训练了500轮,每轮500步后,效果竟然意外地还不错。一百多轮的时候,小车突然开窍,之后就不会一上来直接摔了。这里训练能坚持的step依然很低是因为有随机噪声。说来也神奇,大多数时候小车左右不停乱晃来保持平衡,有时会突然训练到一个很平滑很自然的状态上去。
这里运气不错,700轮训到了一个不错的结果。
我一开始担心倒双摆过于复杂,于是希望从低重力高阻力的环境开始训练。但似乎是多虑了(浪费了不少时间)。
训练代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
env = gym.make('InvertedDoublePendulum-v5')
# env.env.env.env.model.opt.gravity = [0, 0, -GRAVITY]
# env.env.env.env.model.dof_damping[:] = DAMPING
print(env.env.env.env.model.opt.gravity)
print(env.env.env.env.model.dof_damping)
all_rewards = []
all_steps = []
for episode in range(200):
state = env.reset()[0]
agent.noise.reset()
episode_reward = 0
for step in range(500):
action = agent.choose_action(state)
action = np.clip(action, -action_bondary, action_bondary)
next_state, reward, t1, t2, _ = env.step(action)
done = t1 or t2
# reward = (reward - 8.8 - np.abs(state[5]) * 0.15 - np.abs(state[0]) * 0.3) / 2
# if step > 100:
# reward += 0.04 * step / 500 + 0.03
# if np.abs(state[0]) > 0.1:
# reward -= 0.5 * max(0, (np.abs(state[0]) - 0.1))
# if np.abs(state[5]) > 1:
# reward -= 0.05 * max(0, (np.abs(state[5]) - 1))
# reward = reward if reward > -3 else -3
episode_reward += reward
agent.buffer.push(state, action, reward, next_state, float(done))
state = next_state
agent.learn()
if done:
break
all_rewards.append(episode_reward)
all_steps.append(step)
print(f"Episode {episode}, Reward: {episode_reward:.2f}, {step=}, average_reward_per_step:{episode_reward/(step+1):.2f}")
env.close()
我还尝试降低了OU噪声的幅度,修改奖励使之侧重稳定在中间。有时候梯度消失在奖励上做个平移缩放就能解决问题。说实话奖励的设置有点玄学。
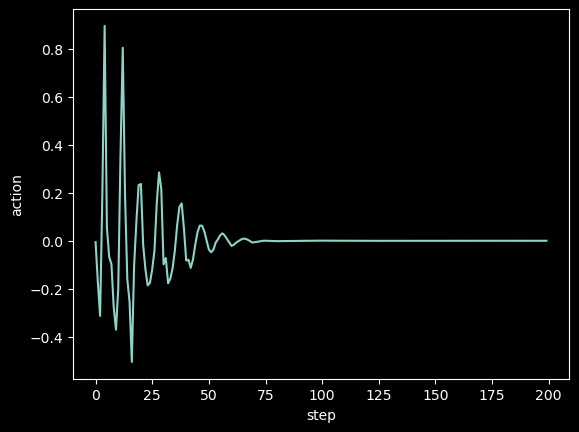
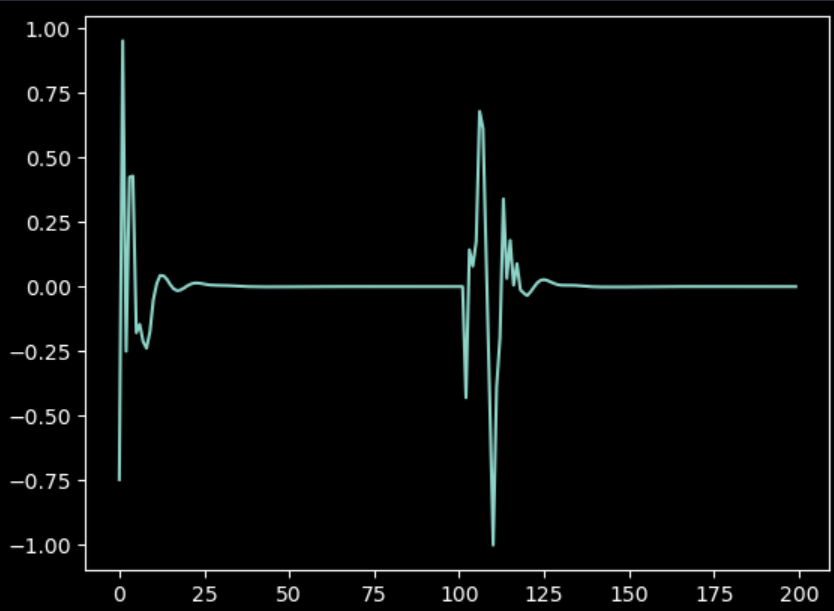
最后训练的结果基本满意,这里env.env.env.env.data.xfrc_applied似乎是一个4*6的矩阵,4似乎分别代表地面(?)、小车、下面的杆、上面的杆,6分别代表xyz方向上的力和xyz轴向上的力矩。给上面的杆施加一个角冲量,小车依然能自行恢复稳定。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
env = gym.make('InvertedDoublePendulum-v5', render_mode='human')
# env.env.env.env.model.opt.gravity = [0, 0, -GRAVITY]
# env.env.env.env.model.dof_damping[:] = DAMPING
all_actions = []
for episode in range(3):
state = env.reset()[0]
for step in range(500):
if 100 < step < 105:
env.env.env.env.data.xfrc_applied[3] = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0])
else:
env.env.env.env.data.xfrc_applied[3] = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
env.render()
time.sleep(0.02)
action = agent.choose_action(state, False)
all_actions.append(action)
next_state, reward, done, _, _ = env.step(action)
state = next_state
if done:
break
print(f"{episode=}, {step=}")
env.close()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
# OU噪声
class OUNoise:
def __init__(self, size, mu=0.0, theta=0.15, sigma=0.2):
self.size = size
self.mu = mu
self.theta = theta
self.sigma = sigma
self.reset()
def reset(self):
self.state = np.ones(self.size) * self.mu
def sample(self):
dx = self.theta * (self.mu - self.state) + self.sigma * np.random.randn(self.size)
self.state += dx
return self.state
# 经验回放
class ReplayBuffer:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.buffer = deque(maxlen=capacity)
def push(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.buffer.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))
def sample(self, batch_size):
batch = random.sample(self.buffer, batch_size)
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = map(np.array, zip(*batch))
return states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones
def __len__(self):
return len(self.buffer)
# Actor网络
class Actor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, max_action):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(state_dim, 400), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(400, 300), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(300, action_dim), nn.Tanh()
)
self.max_action = max_action
def forward(self, state):
return self.max_action * self.net(state)
# Critic网络
class Critic(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(state_dim + action_dim, 400), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(400, 300), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(300, 1)
)
def forward(self, state, action):
x = torch.cat([state, action], 1)
return self.net(x)
class DDPG:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, action_bondary, actor_lr, critic_lr, batch_size, gamma, tau):
self.actor = Actor(state_dim, action_dim, action_bondary)
self.actor_target = Actor(state_dim, action_dim, action_bondary)
self.actor_target.load_state_dict(self.actor.state_dict())
self.actor_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.actor.parameters(), lr=actor_lr)
self.critic = Critic(state_dim, action_dim)
self.critic_target = Critic(state_dim, action_dim)
self.critic_target.load_state_dict(self.critic.state_dict())
self.critic_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.critic.parameters(), lr=critic_lr)
self.buffer = ReplayBuffer(50000)
self.noise = OUNoise(action_dim)
self.action_bondary = action_bondary # 动作空间的范围是[-action_bondary, action_bondary]
self.batch_size = batch_size # 每轮更新从经验回放中抽出的样本数
self.gamma = gamma # 时序差分目标的折现因子
self.tau = tau # 软更新的比例
def choose_action(self, state, noise=True):
state = torch.FloatTensor(state).unsqueeze(0)
action = self.actor(state).detach().numpy()[0]
if noise:
action += self.noise.sample()
return action
def learn(self):
if len(self.buffer) < self.batch_size:
return
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = self.buffer.sample(self.batch_size)
states = torch.FloatTensor(states)
actions = torch.FloatTensor(actions)
rewards = torch.FloatTensor(rewards).unsqueeze(1)
next_states = torch.FloatTensor(next_states)
dones = torch.FloatTensor(dones).unsqueeze(1)
# 更新Critic网络
with torch.no_grad():
next_actions = self.actor_target(next_states)
target_q = self.critic_target(next_states, next_actions)
target_q = rewards + (1 - dones) * self.gamma * target_q
current_q = self.critic(states, actions)
critic_loss = nn.MSELoss()(current_q, target_q)
self.critic_optimizer.zero_grad()
critic_loss.backward()
self.critic_optimizer.step()
# 更新Actor网络
now_actions = self.actor(states)
actor_loss = -self.critic(states, now_actions).mean()
self.actor_optimizer.zero_grad()
actor_loss.backward()
self.actor_optimizer.step()
# 软更新目标网络
for param, target_param in zip(self.critic.parameters(), self.critic_target.parameters()):
target_param.data.copy_(self.tau * param.data + (1 - self.tau) * target_param.data)
for param, target_param in zip(self.actor.parameters(), self.actor_target.parameters()):
target_param.data.copy_(self.tau * param.data + (1 - self.tau) * target_param.data)